Here’s everything you need to know about what zebras eat and their diet.
Zebras thrive on a unique diet that helps them survive in the wild, even in harsh environments.
In this guide, you’ll dive into the fascinating world of zebra nutrition and diet essentials.
You’ll learn:
- What zebras eat in the wild versus captivity
- How their specialized digestive system works
- The challenges they face finding food
- Nutritional benefits of their fibrous diet
- How zebras adapt to environmental changes
End of this guide, you’ll understand why zebras are such resilient grazers and how their diet helps them survive in the wild. Let’s jump in!
Learn more about zebras in our detailed Zebra Overview article.
1. What is the Typical Diet of a Zebra?
Zebras primarily rely on a plant-based diet, but what exactly are they eating daily?
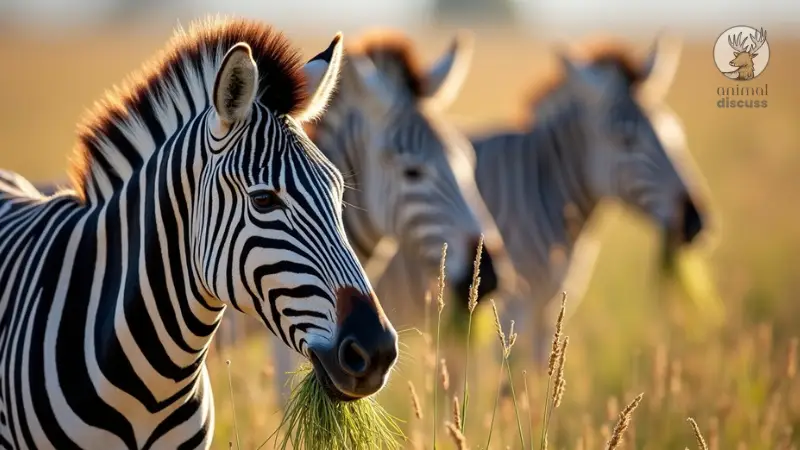

Let’s explore the foundational aspects of their diet, focusing on the most common sources of food.
Do Zebras Primarily Eat Grass?
Yes, zebras are grazing herbivores, and their main source of food is grass.
They spend a significant portion of their day grazing, which is critical for maintaining their energy levels.
However, not all grasses are the same, and zebras have preferences for certain types depending on the region they inhabit.
What Types of Grasses are Common in a Zebra’s Diet?
In their natural habitat, zebras prefer tall, tough grasses that many other herbivores avoid.
This is because their digestive systems are designed to process large amounts of low-nutrient food, such as savanna grasses like red oat grass and Bermuda grass.
These grasses grow in abundance in the African savannas, which make up the primary range for zebras.
Do Zebras Eat Different Plants Depending on the Season?
Yes, seasonal changes directly impact zebras’ food sources.
During the wet season, when grasses are lush and abundant, zebras primarily consume them.
However, in the dry season, grasses become scarce, and zebras will turn to other types of vegetation like shrubs, leaves, and even tree bark.
This shift in diet is crucial for their survival during periods when food is less available.
2. Do Zebras Eat Other Plants Besides Grass?
While grass makes up the bulk of a zebra’s diet, they aren’t limited to it. Zebras are adaptable feeders and will consume other types of plants when necessary.
Can Zebras Eat Shrubs and Herbs?
Yes, shrubs and herbs are part of a zebra’s diet, especially in times when grasses are in short supply.
These plants provide an alternative source of nutrition, helping zebras meet their dietary needs.

While grasses are high in fiber, shrubs and herbs offer more variety in terms of nutrients.
How Do Zebras’ Diets Change in Areas with Scarce Grass?
In areas where grass is less abundant, zebras will eat woody plants, bushes, and sometimes even roots.
Zebras have evolved to survive in different environments, from savannas to mountainous regions, which means they have to adapt to a wider range of plant life.
Do Zebras Eat Fruits or Vegetables in the Wild?
Zebras don’t typically eat fruits or vegetables as part of their diet in the wild.
Their natural habitat doesn’t provide much of these, and their digestive system is more suited to processing high-fiber foods like grasses.
However, in rare cases, zebras may consume wild fruits if available, especially during droughts or food scarcity, but it’s not a primary part of their diet.
3. How Do Zebras Adapt Their Diet to Different Environments?
Zebras are found in various environments, from open grasslands to more arid regions, which presents different challenges in terms of food availability.
Understanding how they adapt to these environments is key to understanding their overall diet.
How Do Zebras Find Food in Dry or Arid Regions?
In dry regions, where grass is not as readily available, zebras will often travel great distances to find food.
They are known to migrate during extreme weather conditions, moving in large herds to areas with better grazing conditions.
Adaptability is essential for survival, and zebras are excellent at finding food even in challenging environments.
Do Zebras Migrate to Find Better Food Sources?
Yes, migration plays a significant role in the diet of many zebra species, especially the plains zebra.
During dry seasons, zebras travel with other herbivores like wildebeest in search of food and water.
This migration ensures they always have access to enough grass, even if it means moving hundreds of miles.
What Role Does Water Availability Play in a Zebra’s Diet?
Water is a critical component of a zebra’s diet. Without sufficient water, even the best grazing areas aren’t enough.
Zebras are never found too far from a water source, and during extreme droughts, they’ll migrate to find areas with both grass and water.
In fact, water availability often dictates where zebras feed, as dehydration can be just as dangerous as starvation.
4. How Does a Zebra’s Digestive System Work?
Understanding how zebras process their food is key to grasping why they can survive on a diet that consists primarily of tough grasses.
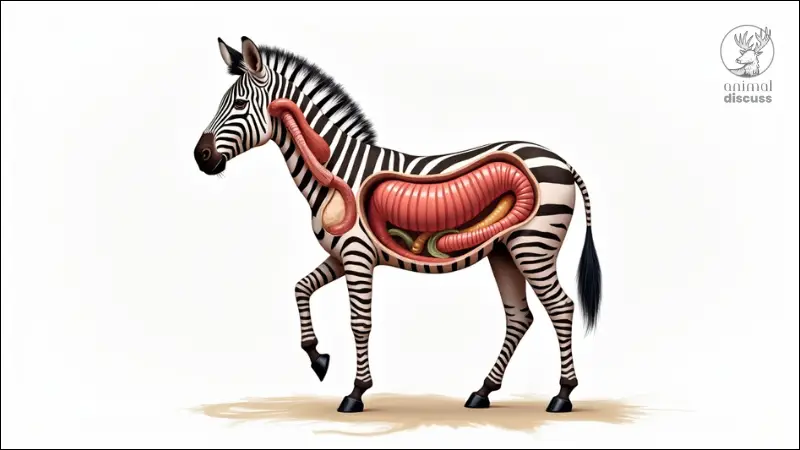
Zebras have a highly specialized digestive system that allows them to make the most out of their plant-based diet, even though grasses are not highly nutritious.
How Do Zebras Digest Fibrous Plant Material?
Zebras are hindgut fermenters, meaning they digest food in their large intestine and cecum.
This process helps them break down the tough, fibrous grasses they eat.
Unlike ruminants, such as cows, zebras do not chew cud. Instead, they rely on microbes in their hindgut to ferment and break down the plant material, extracting as many nutrients as possible from the food.
What Is Hindgut Fermentation, and How Does It Help Zebras Process Their Food?
Hindgut fermentation is a digestive process where microbes in the large intestine break down cellulose (a major component of plant cell walls).
This allows zebras to extract energy and nutrients from fibrous grasses that many other herbivores cannot digest as efficiently.
While this method of digestion isn’t as thorough as ruminant digestion, it’s faster, allowing zebras to consume large amounts of grass quickly and move on to new feeding grounds.
How Efficient Is a Zebra’s Digestion Compared to Other Herbivores?
While zebras’ digestion is not as efficient as that of ruminants (like antelopes or cattle), it’s fast and enables them to consume greater quantities of lower-quality food.
This gives them an advantage in areas where food is abundant but not particularly nutrient-rich.
Zebras can graze for hours, filling their stomachs with grass, then move to another area to continue eating, which keeps them constantly fueled.
5. What Is the Nutritional Value of a Zebra’s Diet?
Zebras may spend the majority of their day grazing, but what exactly are they getting out of their food?
Although grass is not the most nutrient-dense food, it provides the basic requirements zebras need to survive.
How Much Protein and Fiber Do Zebras Get from Their Diet?
Grasses are low in protein but high in fiber, which forms the bulk of a zebra’s diet.
Fiber is essential for keeping their digestive systems functioning smoothly, while protein helps with muscle maintenance and overall body function.
Although their diet isn’t high in protein, zebras eat enough grass to meet their basic nutritional needs.
What Minerals and Vitamins Are Essential for a Zebra’s Health?
In addition to protein and fiber, zebras also need essential minerals like calcium and phosphorus, which they get from grazing on specific types of grass and other plants.
These minerals are crucial for maintaining strong bones and overall health.
Zebras may also seek out salt licks or mineral-rich areas to compensate for any dietary deficiencies.
How Do Zebras Maintain Energy with Low-Calorie Foods Like Grass?
Even though grass is low in calories compared to other foods, zebras compensate by grazing for long periods throughout the day.
Their digestive systems allow them to extract energy from these fibrous foods, and by eating constantly, they can maintain their energy levels despite the low caloric intake.
6. Do Zebras Need Supplements or Special Foods in Captivity?
In the wild, zebras have access to a variety of grasses and plants, but in captivity, their diet needs to be managed carefully to ensure they get all the nutrients they require.
Zoos and sanctuaries must mimic a zebra’s natural diet as closely as possible to maintain their health.
What Do Zebras Eat in Zoos?
In zoos, zebras are typically fed a diet that includes hay, grains, and specialized pellets designed to mimic their natural diet.
Alfalfa and timothy hay are common in zoo environments because they closely resemble the types of grasses zebras would eat in the wild.
These hays provide a good balance of fiber, protein, and essential nutrients.
How Is Their Diet Managed to Ensure Proper Nutrition in Captivity?
Zookeepers carefully monitor the nutritional intake of zebras to ensure they are getting enough fiber, protein, and minerals.
They often supplement their diets with vitamin and mineral blocks, which help zebras meet their nutritional needs without overfeeding.
This management is crucial because zebras in captivity don’t have the same freedom to graze all day like they do in the wild.
Do Zebras in Captivity Require Supplements to Mimic Their Natural Diet?
Yes, in most cases, zebras in captivity require supplements to ensure they get all the necessary nutrients. These can include calcium, phosphorus, and salt, which are sometimes lacking in the artificial diets provided.
Additionally, in some cases, zoos will offer zebras browsing opportunities-allowing them to eat branches and leaves-to better mimic the variety they would have in the wild.
7. What Challenges Do Zebras Face in Finding Food?
While zebras are adaptable eaters, they face several challenges in the wild that can impact their ability to find food.

From environmental changes to human activity, these factors can affect their access to the food they need.
How Do Droughts or Habitat Loss Impact Zebra Feeding Habits?
Droughts are one of the biggest challenges for zebras in the wild.
When water sources dry up and grasses become scarce, zebras are forced to travel great distances to find food.
Habitat loss, due to human encroachment and farming, also limits their grazing areas, making it harder to find enough food to sustain their herds.
These challenges put zebras at risk of starvation and malnutrition, especially during prolonged dry periods.
Are Zebras Competing with Other Animals for Food Sources?
Yes, zebras often have to compete with other herbivores, such as wildebeest and antelope, for the same food sources.
In some areas, this competition can be fierce, particularly during the dry season when grasses are scarce.
Zebras’ ability to eat tougher, less nutrient-dense grasses gives them an advantage, but they still face stiff competition for the best grazing spots.
How Do Human Activities Like Farming Affect Zebras’ Access to Food?
Human activities, especially agriculture, can have a significant impact on zebra populations.
As more land is cleared for farming, zebras lose their natural grazing grounds, which forces them to migrate or survive on smaller patches of land.
In some cases, zebras may even come into conflict with humans as they graze on crops, which can lead to dangerous encounters.
Final Words
Zebras may seem like simple grazers, but their diet and digestive systems are uniquely adapted to help them thrive in the wild.
Their ability to extract nutrients from tough grasses allows them to survive even in challenging environments.
From grasslands to captivity, zebras rely on fibrous plants and their specialized hindgut fermentation to meet their nutritional needs.
Their resilience in finding food, despite competition and environmental changes, showcases their adaptability.
In short, understanding a zebra’s diet is key to appreciating their survival strategies.
References
- African Wildlife Foundation. (n.d.). Zebra.
- Smithsonian National Zoo. (n.d.). Zebra Diet.
- IUCN. (2002). Equids: Zebras, Asses, and Horses.
- Rubenstein, D. I. (2010). Zebra behavior and ecology. Adv. Study Behav., 42, 231–258.

